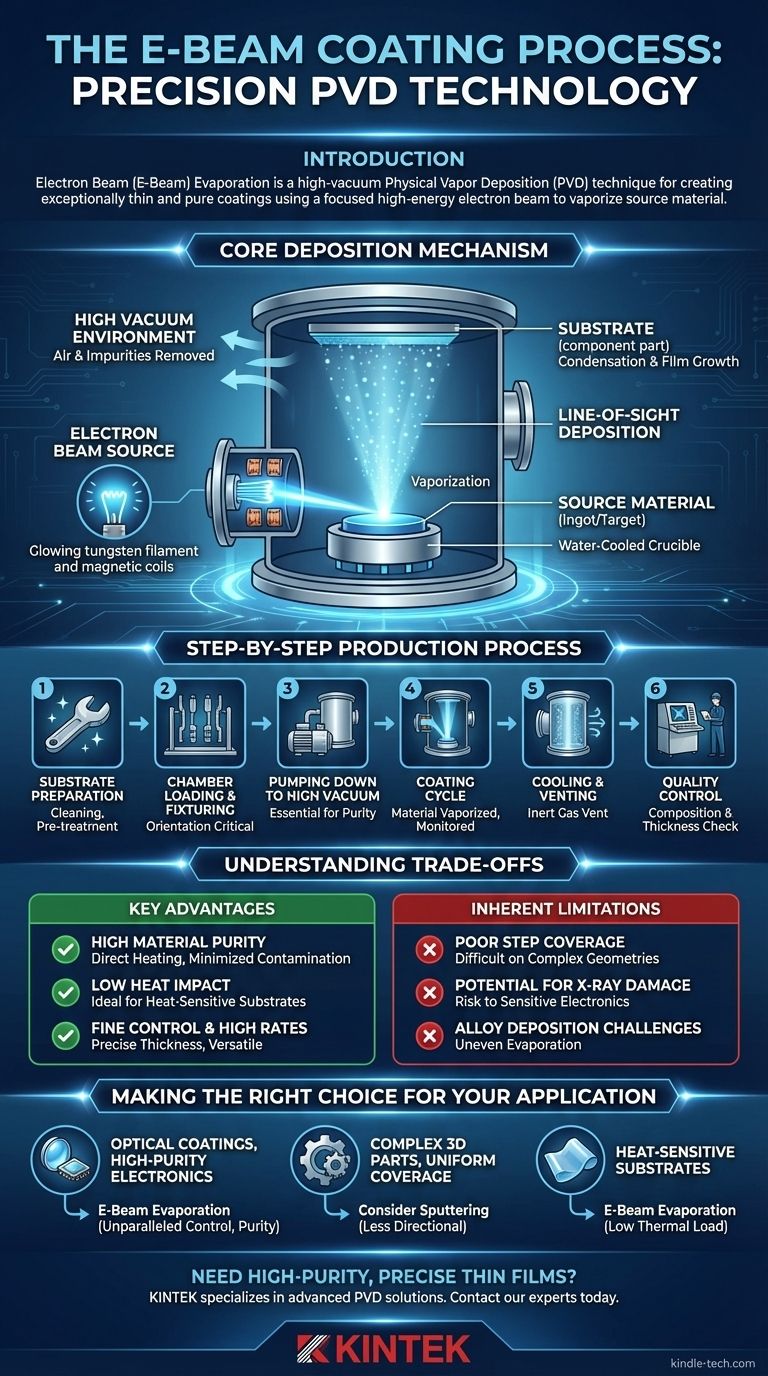
التبخير بالحزمة الإلكترونية (E-Beam) هو تقنية ترسيب فيزيائي بالبخار (PVD) عالية التفريغ تُستخدم لإنشاء طلاءات رقيقة ونقية بشكل استثنائي. تستخدم العملية حزمة إلكترونات مركزة وعالية الطاقة لتسخين مادة المصدر، مما يؤدي إلى تبخيرها. ينتقل هذا البخار بعد ذلك في خط مستقيم ويتكثف على ركيزة، مكونًا طبقة دقيقة، ذرة بذرة.
يُعد طلاء الحزمة الإلكترونية عملية ترسيب خطية أساسًا، تُقدر لدقتها وتأثيرها الحراري المنخفض على المكون الذي يتم طلاؤه. تتفوق في إنشاء أغشية نقية وكثيفة للغاية للتطبيقات المتخصصة، لكن طبيعتها الاتجاهية تمثل تحديات لطلاء الأشكال الهندسية ثلاثية الأبعاد المعقدة.

آلية الترسيب الأساسية
لفهم عملية الحزمة الإلكترونية، من الضروري فهم الفيزياء الأساسية التي تحدث داخل غرفة التفريغ. يتم التحكم في كل خطوة بدقة لتحقيق تركيبة وسمك معين للفيلم.
بيئة التفريغ
تحدث العملية بأكملها داخل غرفة تفريغ عالية. يُعد إخلاء الغرفة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لإزالة الهواء والشوائب الغازية الأخرى التي قد تتفاعل مع المادة المتبخرة وتلوث الفيلم النهائي. تسمح حالة شبه التفريغ هذه أيضًا لذرات البخار بالانتقال مباشرة إلى الركيزة دون الاصطدام بجزيئات أخرى.
مصدر الحزمة الإلكترونية
يتم تسخين فتيل التنجستن لتوليد تيار من الإلكترونات. ثم يتم تسريع هذه الإلكترونات وتركيزها في حزمة عالية الطاقة باستخدام سلسلة من المجالات المغناطيسية، على غرار طريقة عمل تلفزيون أنبوب الأشعة الكاثودية (CRT).
تبخير مادة المصدر
يتم توجيه حزمة الإلكترونات المركزة هذه إلى مادة المصدر (التي غالبًا ما تسمى سبيكة أو هدفًا)، والتي تُحفظ في بوتقة نحاسية مبردة بالماء. تعمل الطاقة المكثفة من الحزمة على تسخين المادة إلى نقطة غليانها، مما يؤدي إلى تبخرها أو تساميها إلى بخار.
الترسيب بخط الرؤية
تنتقل ذرات البخار في مسار مستقيم ومباشر من المصدر إلى الركيزة. تعني هذه الخاصية "خط الرؤية" أن الطلاء يترسب فقط على الأسطح المرئية مباشرة من مصدر التبخير.
التكثيف ونمو الفيلم
عندما تصل ذرات البخار إلى السطح البارد نسبيًا للركيزة، فإنها تتكثف. تبني هذه العملية طبقة الطلاء طبقة تلو الأخرى، ذرة بذرة، مما ينتج عنه فيلم رقيق دقيق الحبيبات وكثيف للغاية.
عملية الإنتاج خطوة بخطوة
يتضمن الانتقال من الآلية الأساسية إلى التطبيق الصناعي سلسلة من خطوات الإنتاج المدارة بعناية.
الخطوة 1: تحضير الركيزة
الالتصاق الصحيح مستحيل بدون سطح نقي. تتضمن هذه الخطوة تنظيفًا دقيقًا لإزالة أي ملوثات. اعتمادًا على تاريخ الجزء، قد يتضمن أيضًا إزالة الطلاءات القديمة أو معالجات مسبقة محددة لتحضير السطح.
الخطوة 2: تحميل الغرفة والتثبيت
توضع مادة المصدر في بوتقتها، وتُثبت الركائز على تركيبات أو حاملات متخصصة. يُعد توجيه هذه التركيبات أمرًا بالغ الأهمية نظرًا لطبيعة عملية خط الرؤية، مما يضمن تعرض الأسطح المستهدفة بشكل صحيح لتيار البخار.
الخطوة 3: الضخ إلى تفريغ عالٍ
بمجرد التحميل، تُغلق الغرفة وتُفرغ إلى مستوى ضغط مستهدف. يمكن أن يستغرق هذا الضخ وقتًا طويلاً ولكنه ضروري لنقاء الطلاء النهائي.
الخطوة 4: دورة الطلاء
مع إنشاء التفريغ، يتم تنشيط حزمة الإلكترونات، وتبخير المادة. تتم مراقبة معدل الترسيب والسمك النهائي في الوقت الفعلي لضمان أن الفيلم يلبي المواصفات الدقيقة. يمكن أن تتراوح الدورة بأكملها من ثلاثين دقيقة إلى عدة ساعات اعتمادًا على المادة والسمك المطلوب.
الخطوة 5: التبريد والتهوية
بعد الوصول إلى السمك المستهدف، يتم إلغاء تنشيط حزمة الإلكترونات. يُسمح للنظام بالتبريد قبل تهوية الغرفة بغاز خامل، وإعادتها إلى الضغط الجوي.
الخطوة 6: مراقبة الجودة
تخضع كل دفعة لفحص دقيق. يستخدم الفنيون أدوات مثل جهاز الفلورسنت بالأشعة السينية (XRF) للتحقق من تركيبة الطلاء وسمكه، مما يضمن استيفائه لجميع المعايير المطلوبة.
فهم المفاضلات
لا توجد تقنية طلاء واحدة مثالية لكل تطبيق. يتمتع التبخير بالحزمة الإلكترونية بمزايا وقيود مميزة تحدد حالات استخدامه المثالية.
المزايا الرئيسية
- نقاء المواد العالي: تسخن حزمة الإلكترونات مادة المصدر فقط مباشرة، وليس البوتقة بأكملها، مما يقلل من التلوث وينتج أغشية نقية بشكل استثنائي.
- تأثير حراري منخفض: تنقل العملية حرارة أقل إلى الركيزة مقارنة بالطرق الأخرى، مما يجعلها مثالية لطلاء المواد الحساسة للحرارة مثل البلاستيك أو البوليمرات أو المكونات الإلكترونية المجمعة مسبقًا.
- تحكم دقيق ومعدلات عالية: يسمح بتحكم دقيق للغاية في معدل الترسيب وسمك الفيلم، بينما يكون قادرًا أيضًا على تحقيق معدلات تبخير عالية جدًا لمجموعة واسعة من المواد، بما في ذلك المعادن والسيراميك.
القيود المتأصلة
- تغطية ضعيفة للخطوات: يجعل تيار البخار عالي الاتجاه من الصعب طلاء الأشكال المعقدة أو الحواف الحادة أو الأسطح الداخلية بشكل موحد. يغطي بشكل أساسي ما يمكنه "رؤيته".
- احتمال تلف الأشعة السينية: يمكن أن يؤدي تفاعل الإلكترونات عالية الطاقة مع مادة المصدر إلى توليد الأشعة السينية. على الرغم من أنها عادةً ما تكون منخفضة المستوى، إلا أنها يمكن أن تكون كافية لإتلاف الركائز الإلكترونية الحساسة للغاية أو المكونات البصرية.
- تحديات ترسيب السبائك: قد يكون من الصعب تبخير المواد المصنوعة من عناصر متعددة (السبائك) ذات ضغوط بخار مختلفة، حيث يتبخر العنصر الأكثر تطايرًا أولاً.
اتخاذ القرار الصحيح لتطبيقك
يتطلب اختيار طريقة PVD الصحيحة مواءمة قدرات العملية مع هدفك الهندسي الأساسي.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي على الطلاءات البصرية أو الإلكترونيات عالية النقاء: يوفر التبخير بالحزمة الإلكترونية تحكمًا لا مثيل له في سمك الفيلم ونقائه وكثافته، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية لهذه التطبيقات.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي على طلاء الأجزاء ثلاثية الأبعاد المعقدة بتغطية موحدة: يجب أن تفكر في طرق PVD الأقل اتجاهية مثل التشتيت لضمان طلاء جميع الأسطح بشكل كافٍ.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي على طلاء الركائز الحساسة للحرارة: فإن الحمل الحراري المنخفض لعملية الحزمة الإلكترونية يجعلها خيارًا ممتازًا لحماية المواد مثل البوليمرات أو المكونات الدقيقة المجمعة مسبقًا.
في النهاية، يُعد اختيار التبخير بالحزمة الإلكترونية قرارًا استراتيجيًا للتطبيقات التي تكون فيها جودة الفيلم النهائي ودقته أكثر أهمية من تحقيق تغطية هندسية موحدة.
جدول الملخص:
| الجانب الرئيسي | التفاصيل |
|---|---|
| نوع العملية | الترسيب الفيزيائي بالبخار (PVD) |
| البيئة | تفريغ عالٍ |
| الآلية | الترسيب بخط الرؤية |
| المزايا الرئيسية | نقاء عالٍ، تأثير حراري منخفض، تحكم دقيق في السمك |
| مثالي لـ | الطلاءات البصرية، الإلكترونيات عالية النقاء، الركائز الحساسة للحرارة |
| القيود | تغطية ضعيفة على الأشكال الهندسية ثلاثية الأبعاد المعقدة |
هل تحتاج إلى أغشية رقيقة عالية النقاء والدقة لبحثك أو إنتاجك؟
تتخصص KINTEK في معدات المختبرات المتقدمة، بما في ذلك حلول PVD للتطبيقات الصعبة. يمكن لخبرتنا أن تساعدك في اختيار تقنية الطلاء المناسبة لضمان جودة الفيلم الفائقة والنقاء والأداء لركائزك وأهدافك المحددة.
اتصل بخبرائنا اليوم لمناقشة كيف يمكننا دعم احتياجات مختبرك لترسيب الأغشية الرقيقة.
دليل مرئي
المنتجات ذات الصلة
- نظام ترسيب بخار كيميائي معزز بالبلازما بترددات الراديو RF PECVD
- بوتقة نيتريد البورون الموصلة بالتبخير الشعاعي الإلكتروني، بوتقة BN
- قارب تبخير الموليبدينوم والتنجستن والتنتالوم للتطبيقات ذات درجات الحرارة العالية
- نظام معدات الترسيب الكيميائي للبخار (CVD) - فرن أنبوبي PECVD منزلق مع جهاز تغويز السوائل - ماكينة PECVD
- قارب تبخير التنغستن الموليبدينوم ذو القاع نصف الكروي
يسأل الناس أيضًا
- ما هي عيوب الترسيب الكيميائي للبخار المعزز بالبلازما (PECVD)؟ فهم المفاضلات في الترسيب في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة
- ما هو ترسيب البلازما الكيميائي للبخار (CVD)؟ اكتشف ترسيب الأغشية الرقيقة بدرجة حرارة منخفضة للمواد الحساسة
- ما الفرق بين PECVD و CVD؟ دليل لاختيار عملية ترسيب الأغشية الرقيقة المناسبة
- كيف تخلق طاقة التردد اللاسلكي (RF) البلازما؟ احصل على بلازما مستقرة وعالية الكثافة لتطبيقاتك
- ما هي عيوب ترسيب البخار الكيميائي المعزز بالبلازما؟ إدارة المفاضلات في الترسيب بدرجة حرارة منخفضة


















