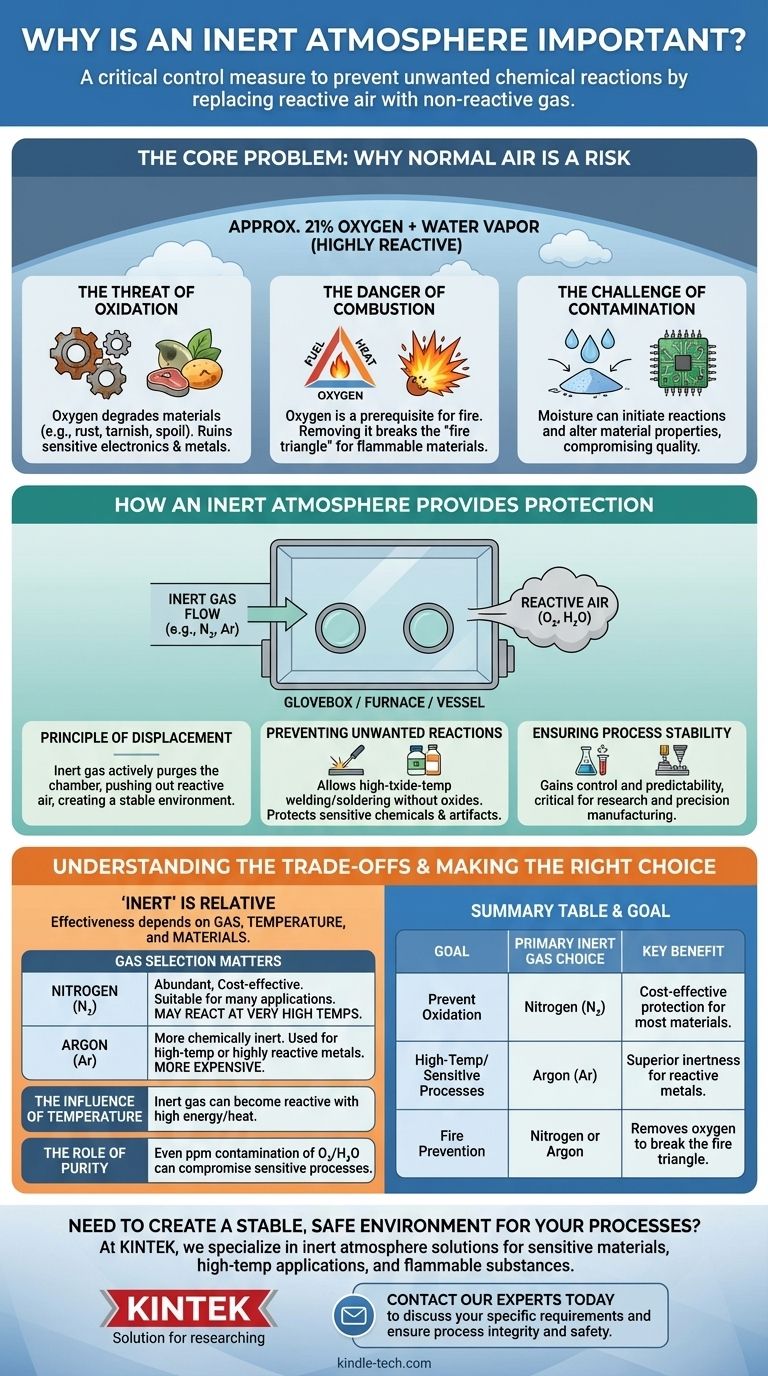
يعتبر الغلاف الجوي الخامل إجراءً رقابياً حاسماً يُستخدم لمنع التفاعلات الكيميائية غير المرغوب فيها. عن طريق استبدال الهواء التفاعلي في مكان العمل - وخاصة الأكسجين وبخار الماء فيه - بغاز غير تفاعلي، فإنك تحمي المواد من التدهور، وتضمن نقاء العملية، وتقضي على خطر الحريق أو الانفجار.
الهواء من حولنا ليس محايداً؛ إنه عامل كيميائي تفاعلي يمكن أن يتلف المواد الحساسة ويعرقل العمليات الدقيقة. يعمل الغلاف الجوي الخامل كدرع واقٍ، مما يخلق بيئة مستقرة حيث يمكن أداء العمل دون خطر التداخل الجوي غير المرغوب فيه.

المشكلة الأساسية: لماذا يمثل الهواء العادي خطراً
لفهم الحل، يجب أن ندرك أولاً المشكلة. الغلاف الجوي القياسي الذي نعيش فيه يتكون من حوالي 21٪ أكسجين ويحتوي على كميات متفاوتة من بخار الماء، وكلاهما شديد التفاعل.
خطر الأكسدة
الأكسجين عدواني. يتفاعل بسهولة مع العديد من المواد في عملية تسمى الأكسدة، مما يؤدي إلى تدهورها.
هذا هو نفس التفاعل الكيميائي الذي يسبب صدأ الحديد، وتآكل النحاس، وتلف الأطعمة. في الإعدادات التقنية أو التصنيعية، يمكن أن تؤدي الأكسدة إلى إتلاف الإلكترونيات الحساسة، وإضعاف المعادن، وتغيير التركيب الكيميائي للمنتج.
خطر الاحتراق
وجود الأكسجين شرط مسبق للحريق. لحدوث الاحتراق، هناك حاجة إلى ثلاثة أشياء: الوقود والحرارة وعامل مؤكسد (عادة الأكسجين).
بإزالة الأكسجين من المعادلة، فإنك تكسر "مثلث النار" هذا. هذا ضروري عند التعامل مع المذيبات القابلة للاشتعال، أو المساحيق المعدنية الدقيقة، أو المواد الأخرى التي يمكن أن تشتعل أو تنفجر في الغلاف الجوي العادي.
تحدي التلوث
بالإضافة إلى الأكسجين، يمكن للمكونات الجوية الأخرى مثل الرطوبة أن تعمل كملوثات. يمكن أن يبدأ بخار الماء تفاعلات غير مرغوب فيها أو يتم امتصاصه بواسطة المواد المسترطبة، مما يغير خصائصها ويعرض جودة المنتج النهائي للخطر.
كيف يوفر الغلاف الجوي الخامل الحماية
يتضمن إنشاء غلاف جوي خامل إزاحة الهواء المحيط بنشاط في بيئة مغلقة - مثل صندوق القفازات، أو الفرن، أو وعاء التفاعل - واستبداله بغاز لن يتفاعل مع المواد الموجودة بالداخل.
مبدأ الإزاحة
الآلية الأساسية بسيطة: يتم استخدام تدفق ثابت من الغاز الخامل لتطهير الحجرة، مما يدفع الهواء الخفيف والتفاعلي إلى الخارج. والنتيجة هي غلاف جوي داخلي يتكون بالكامل تقريباً من الغاز المستقر وغير التفاعلي.
منع التفاعلات غير المرغوب فيها
مع إزالة الأكسجين والرطوبة، تختفي المحركات الرئيسية للتدهور. يتيح ذلك عمليات مثل اللحام أو اللحام في درجات حرارة عالية دون تكوين أكاسيد تضعف الرابطة. كما يسمح بالتخزين طويل الأجل للمواد الكيميائية أو القطع الأثرية الحساسة.
ضمان استقرار العملية
من خلال إزالة متغير التفاعلية الجوية، تكتسب سيطرة أكبر وتنبؤاً بعمليتك. هذا الاستقرار أمر بالغ الأهمية في الأبحاث العلمية والتصنيع عالي الدقة، حيث يمكن أن يؤدي حتى التفاعلات الطفيفة غير المقصودة إلى الفشل.
فهم المفاضلات: "خامل" نسبي
مصطلح "خامل" ليس مطلقاً. تعتمد فعالية الغلاف الجوي الخامل على الغاز المحدد المستخدم، ودرجة حرارة العملية، والمواد المعنية.
اختيار الغاز مهم
الغازات الخاملة الأكثر شيوعاً هي النيتروجين (N₂) والأرغون (Ar). النيتروجين وفير وفعال من حيث التكلفة، مما يجعله مناسباً للعديد من التطبيقات. ومع ذلك، في درجات الحرارة العالية جداً، يمكن أن يتفاعل مع بعض المعادن لتكوين نتريدات.
الأرغون أكثر خمولاً كيميائياً من النيتروجين وغالباً ما يستخدم في العمليات ذات درجات الحرارة العالية أو مع المعادن شديدة التفاعل حيث يكون النيتروجين غير مناسب. ومع ذلك، فهو أغلى بكثير.
تأثير درجة الحرارة
يمكن للغاز الذي يكون خاملاً في درجة حرارة الغرفة أن يصبح تفاعلياً عند إدخال طاقة كافية، مثل الحرارة العالية. هذا هو السبب في أن المادة ودرجة الحرارة عاملان حاسمان عند اختيار الغاز الخامل المناسب للفرن أو تطبيق اللحام.
دور النقاء
نقاء الغاز الخامل أمر بالغ الأهمية. حتى بضعة أجزاء في المليون من تلوث الأكسجين أو الرطوبة في إمداد الغاز يمكن أن تكون كافية لتعريض عملية حساسة للغاية للخطر.
اتخاذ الخيار الصحيح لهدفك
يعتمد اختيار الضوابط الجوية المناسبة بالكامل على هدفك، وموازنة التكلفة مقابل المستوى المطلوب من الحماية.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي هو منع الأكسدة العام: غالباً ما يكون النيتروجين هو الخيار الأكثر عملية وفعالية من حيث التكلفة للعديد من المواد والعمليات.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي هو المواد عالية الحرارة أو شديدة الحساسية: يوفر الأرغون درجة فائقة من الخمول، مما يضمن الحماية حتى عندما قد يتفاعل النيتروجين.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي هو السلامة ومنع الحريق: فإن إزاحة الأكسجين بأي غاز خامل شائع هو الاستراتيجية الأساسية للقضاء على خطر الاحتراق.
من خلال التحكم المتعمد في الغلاف الجوي، تكتسب السيطرة المطلقة على سلامة ونوعية وعمل عملك.
جدول ملخص:
| الهدف | اختيار الغاز الخامل الأساسي | الفائدة الرئيسية |
|---|---|---|
| منع الأكسدة | النيتروجين (N₂) | حماية فعالة من حيث التكلفة لمعظم المواد |
| العمليات عالية الحرارة/الحساسة | الأرغون (Ar) | خمول فائق للمعادن التفاعلية |
| منع الحريق | النيتروجين أو الأرغون | يزيل الأكسجين لكسر مثلث النار |
هل تحتاج إلى إنشاء بيئة مستقرة وآمنة لعملياتك؟
في KINTEK، نحن متخصصون في توفير معدات المختبرات والخبرة المناسبة لتنفيذ حلول الغلاف الجوي الخامل الفعالة - سواء كنت تعمل بمواد حساسة، أو تطبيقات ذات درجات حرارة عالية، أو مواد قابلة للاشتعال. يمكن لفريقنا مساعدتك في اختيار النظام الأمثل لحماية عملك من مخاطر الأكسدة والتلوث والاحتراق.
اتصل بخبرائنا اليوم لمناقشة متطلباتك المحددة وضمان سلامة ونزاهة عمليات المختبر الخاصة بك!
دليل مرئي
المنتجات ذات الصلة
- فرن جو متحكم فيه بدرجة حرارة 1400 درجة مئوية مع غاز النيتروجين والجو الخامل
- فرن جو متحكم فيه بدرجة حرارة 1200 درجة مئوية فرن جو خامل بالنيتروجين
- فرن جو متحكم فيه بدرجة حرارة 1700 درجة مئوية فرن جو خامل نيتروجين
- فرن غاز خامل بالنيتروجين المتحكم فيه
- فرن أنبوبي مختبري بدرجة حرارة عالية 1400 درجة مئوية مع أنبوب ألومينا
يسأل الناس أيضًا
- لماذا يستخدم النيتروجين في الفرن؟ درع فعال من حيث التكلفة للعمليات عالية الحرارة
- كيف يمكننا تطوير جو خامل لتفاعل كيميائي؟ إتقان التحكم الدقيق في الغلاف الجوي لمختبرك
- ما هو دور النيتروجين في عملية التلدين؟ خلق جو متحكم فيه ووقائي
- ما هي وظائف النيتروجين (N2) في أجواء الأفران المتحكم بها؟ تحقيق نتائج معالجة حرارية فائقة
- ما هي الغازات المستخدمة في الأجواء الخاملة؟ اختر الغاز المناسب للبيئات غير التفاعلية



















