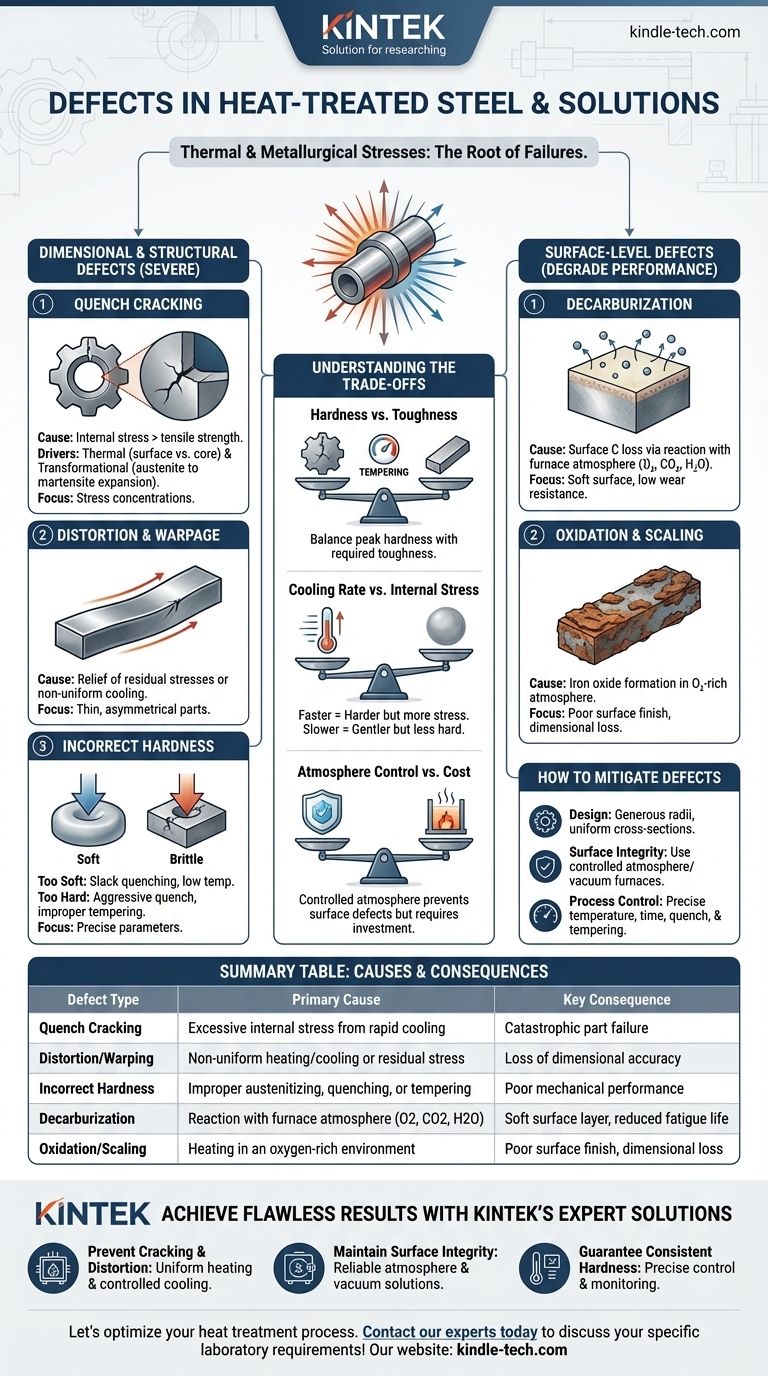
تحدث العيوب في الفولاذ المعالج حرارياً بشكل أساسي بسبب الإجهادات الحرارية والمعدنية الهائلة التي تحدث أثناء التسخين والتبريد السريع. العيوب الأكثر شيوعاً هي التشقق، والتشوه (الالتواء)، والتغيرات السطحية غير المرغوب فيها مثل إزالة الكربنة والتآكل، والفشل في تحقيق الصلابة أو البنية المجهرية المستهدفة. هذه الإخفاقات ليست عشوائية ولكنها نتائج مباشرة لمعلمات العملية التي لم يتم التحكم فيها بشكل صحيح.
عيوب المعالجة الحرارية هي نتائج متوقعة للإجهاد الحراري، والتحولات الطورية، والتفاعلات الكيميائية الجوية. يعتمد منعها على التحكم الصارم في معدل تغير درجة الحرارة، وجو الفرن، وهندسة الجزء من مرحلة التصميم فصاعداً.

فشل الأبعاد والهيكل
تؤثر العيوب الأكثر خطورة على السلامة الميكانيكية والدقة الأبعاد للمكون، مما يجعله غالباً غير صالح للاستخدام.
تشقق التبريد
تشقق التبريد هو أخطر عيب في المعالجة الحرارية. يحدث عندما تتجاوز الإجهادات الداخلية الناتجة عن التبريد قوة الشد القصوى للمادة.
يحدث هذا بسبب قوتين رئيسيتين: الإجهاد الحراري الناتج عن تبريد السطح بشكل أسرع بكثير من اللب، وإجهاد التحول الناتج عن التمدد الذي يحدث عندما يتحول الأوستينيت إلى مارتينسايت هش.
تنشأ الشقوق عادةً عند نقاط تركيز الإجهاد مثل الزوايا الحادة، أو مجاري المفاتيح، أو التغيرات المفاجئة في المقطع العرضي للجزء.
التشوه والالتواء
التشوه هو تغيير لا رجعة فيه في حجم أو شكل المكون يحدث أثناء المعالجة الحرارية.
غالباً ما يحدث هذا بسبب تخفيف الإجهادات المتبقية الناتجة أثناء خطوات التصنيع السابقة (مثل التشغيل الآلي) أو بسبب التسخين والتبريد غير المنتظم. الأجزاء الرقيقة أو الطويلة أو غير المتماثلة معرضة بشكل خاص للالتواء.
صلابة غير صحيحة
غالباً ما يكون تحقيق الصلابة الصحيحة هو الهدف الأساسي، وقد يكون الفشل هنا بسبب عدة عوامل.
قد يكون الجزء ناعم جداً نتيجة لدرجة حرارة أوستنة أو وقت غير كافٍ، أو تبريد كان بطيئاً جداً لقابلية تصلب الفولاذ (المعروف باسم التبريد البطيء).
على العكس من ذلك، غالباً ما يكون الجزء صلباً وهشاً جداً نتيجة لتبريد شديد العدوانية أو، بشكل أكثر شيوعاً، خطوة تلطيف غير صحيحة أو مفقودة بعد التصلب.
عيوب على مستوى السطح
تؤدي هذه العيوب إلى تدهور سطح الفولاذ، مما يضر بأدائه في التطبيقات التي تتطلب مقاومة عالية للتآكل أو قوة إجهاد.
إزالة الكربنة
إزالة الكربنة هي فقدان الكربون من سطح الفولاذ. هذه مشكلة كبيرة لأن الكربون هو العنصر الأساسي المسؤول عن الصلابة في الفولاذ.
يحدث ذلك بسبب تفاعل كيميائي بين الفولاذ وجو الفرن (الأكسجين، ثاني أكسيد الكربون، بخار الماء) عند درجات حرارة عالية. والنتيجة هي طبقة سطحية ناعمة وضعيفة تقلل بشكل كبير من مقاومة التآكل وعمر الإجهاد.
الأكسدة والتآكل
الأكسدة هي تكوين طبقة من أكسيد الحديد (القشور) على سطح المكون عند تسخينه في جو غني بالأكسجين.
تؤدي هذه القشور إلى سوء التشطيب السطحي وفقدان الدقة الأبعاد. يمكنها أيضاً عزل الجزء، مما يؤدي إلى تبريد غير منتظم وربما إخفاء عيوب أساسية أكثر خطورة مثل تشققات التبريد.
فهم المفاضلات
يتضمن اختيار عملية المعالجة الحرارية دائماً الموازنة بين العوامل المتنافسة. فهم هذه المفاضلات هو المفتاح لمنع العيوب.
الصلابة مقابل المتانة
المفاضلة الأساسية في المعالجة الحرارية هي أن العمليات التي تخلق صلابة قصوى، مثل التبريد، تخلق أيضاً بنية مجهرية هشة (المارتينسايت غير الملطف).
التلطيف هو الخطوة الأساسية بعد التبريد التي تقلل من هذا الهشاشة والإجهاد الداخلي، مما يمنح المتانة. ومع ذلك، تقلل هذه العملية أيضاً من الصلابة القصوى. يكمن الفن في إيجاد التوازن الدقيق المطلوب للتطبيق.
معدل التبريد مقابل الإجهاد الداخلي
معدل التبريد الأسرع أكثر فعالية في تحقيق الصلابة الكاملة، خاصة في الفولاذ منخفض السبائك.
ومع ذلك، فإن التبريد السريع (على سبيل المثال، باستخدام الماء أو المحلول الملحي) يولد تدرجات حرارية هائلة وإجهاداً داخلياً، مما يزيد بشكل كبير من خطر التشوه والتشقق. التبريد الأبطأ (على سبيل المثال، باستخدام الزيت أو الغاز) يكون ألطف ولكنه قد لا يحقق أقصى صلابة.
التحكم في الجو مقابل التكلفة
يمنع استخدام جو متحكم فيه (مثل الفراغ، النيتروجين، أو الأرجون) إزالة الكربنة والأكسدة تماماً، مما ينتج جزءاً نظيفاً ولامعاً.
ومع ذلك، تتطلب هذه العمليات معدات أكثر تطوراً وتكلفة مقارنة بالتسخين في فرن مفتوح. يجب تبرير التكلفة بمتطلبات سطح المكون.
كيفية التخفيف من عيوب المعالجة الحرارية
يتطلب منع العيوب اتباع نهج منهجي يركز على التصميم، واختيار المواد، والتحكم الدقيق في العملية.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي هو منع التشقق والتشوه: صمم الأجزاء بنصف أقطار واسعة ومقاطع عرضية موحدة، واختر وسيط تبريد أقل شدة مناسباً لقابلية تصلب الفولاذ.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي هو الحفاظ على سلامة السطح: استخدم أفران ذات جو متحكم فيه (مثل الفراغ، الغاز الخامل) أو طلاءات واقية لمنع إزالة الكربنة والتآكل.
- إذا كان تركيزك الأساسي هو تحقيق صلابة متسقة: تأكد من التحكم الدقيق في درجة حرارة الأوستنة، ووقت النقع، وتقليب التبريد، وتابع دائماً بدورة تلطيف مناسبة.
المعالجة الحرارية الناجحة هي عملية هندسية محكومة حيث يحدد البصيرة في التصميم والدقة في التنفيذ الجودة النهائية للمكون.
جدول الملخص:
| نوع العيب | السبب الرئيسي | النتيجة الرئيسية |
|---|---|---|
| تشقق التبريد | إجهاد داخلي مفرط من التبريد السريع | فشل كارثي للجزء |
| التشوه/الالتواء | تسخين/تبريد غير منتظم أو إجهاد متبقي | فقدان الدقة الأبعاد |
| صلابة غير صحيحة | أوستنة أو تبريد أو تلطيف غير صحيح | أداء ميكانيكي ضعيف |
| إزالة الكربنة | التفاعل مع جو الفرن (O2, CO2, H2O) | طبقة سطحية ناعمة، تقليل عمر الإجهاد |
| الأكسدة/التآكل | التسخين في بيئة غنية بالأكسجين | تشطيب سطحي رديء، فقدان الأبعاد |
حقق نتائج خالية من العيوب مع حلول KINTEK الخبيرة
تخلص من عيوب المعالجة الحرارية المكلفة وتأكد من أن مكوناتك الفولاذية تلبي أعلى معايير الصلابة والمتانة والدقة الأبعاد. تتخصص KINTEK في معدات المختبرات والمواد الاستهلاكية الممتازة، وتوفر الأفران الدقيقة وأنظمة التحكم في الجو والدعم الخبير الذي يحتاجه مختبرك لإتقان معالجته الحرارية.
نحن نساعدك على:
- منع التشقق والتشوه: باستخدام معدات مصممة للتسخين المنتظم والتبريد المتحكم فيه.
- الحفاظ على سلامة السطح: من خلال حلول الأفران الموثوقة ذات الجو المتحكم فيه والفراغ.
- ضمان صلابة متسقة: باستخدام أدوات التحكم والمراقبة الدقيقة لدرجة الحرارة.
دعنا نحسن عملية المعالجة الحرارية الخاصة بك. اتصل بخبرائنا اليوم لمناقشة متطلبات مختبرك المحددة!
دليل مرئي
المنتجات ذات الصلة
- فرن معالجة حرارية بالفراغ مع بطانة من ألياف السيراميك
- فرن معالجة حرارية وتلبيد التنجستن بالفراغ بدرجة حرارة 2200 درجة مئوية
- فرن معالجة حرارية بالفراغ وفرن صهر بالحث المغناطيسي
- فرن معالجة حرارية بالفراغ من الموليبدينوم
- فرن التلدين بالتفريغ الهوائي
يسأل الناس أيضًا
- ما هي أجزاء فرن التفريغ؟ دليل للأنظمة الأساسية للمعالجة الحرارية الدقيقة
- ما هو السمك القياسي للطلاء؟ تحسين المتانة، مقاومة التآكل والتكلفة
- ما هي استخدامات أفران التفريغ؟ افتح العنان لأقصى درجات نقاء المواد وأدائها
- ما هي عملية الفرن الفراغي؟ تحقيق النقاء والدقة في المعالجة ذات درجات الحرارة العالية
- لماذا تستخدم المعالجة الحرارية بالتفريغ؟ احصل على مكونات معدنية خالية من العيوب وعالية الأداء



















